This article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of what makes thermal imaging cameras useful, including their working principles, system components, and application advantages.
What Makes Thermal Imaging Cameras Useful?
Article from | Raythink
In modern fields such as smart security and industrial inspection, thermal imaging technology is rapidly advancing and becoming widely adopted. Unlike ordinary visible light cameras, thermal imaging cameras can “see” temperature and penetrate environments where visible light cannot reach, making them a key technology that overcomes visual limitations.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of what makes thermal imaging cameras useful, including their working principles, system components, and application advantages. Additionally, it offers guidance on how to select the right thermal imaging camera and explores future developments, helping you fully grasp how this technology—“making temperature visible”—empowers today’s society.
Working Principle of Infrared Thermal Imaging Cameras
Infrared radiation, also known as infrared light, is an invisible electromagnetic wave located just beyond the visible light spectrum and before microwaves, with a wavelength range approximately between 0.75 micrometers and 1000 micrometers. It is widely present in nature—any object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C) continuously emits infrared radiation. This radiation serves as a crucial source of information, but since the human eye cannot detect infrared radiation, specialized devices—thermal imaging cameras—are needed to “see” it.
Thermal imaging cameras receive the infrared radiation emitted by objects and convert it into visible two-dimensional images. The resulting images represent the distribution of infrared radiation intensity on the surface of the target, which closely corresponds to its actual temperature field.
What makes thermal imaging cameras useful is their ability not only to extend human vision into the infrared spectrum but also to significantly enhance sensitivity to slight temperature differences. They can capture objective data related to an object’s thermal behavior, making infrared thermal imaging cameras essential tools for visualizing the “temperature world.” This technology is widely applied in industrial inspection, security monitoring, scientific research, and many other fields.
Composition of Infrared Imaging Systems
A typical infrared thermal imaging system mainly consists of three parts: the optical system, the infrared detector, and the electronic processing system.
- The optical system focuses and projects the infrared radiation emitted by the target object onto the photosensitive surface of the infrared detector.
- The infrared detector converts the received infrared radiation signals into electrical signals.
- The electronic processing system amplifies and processes these electrical signals, ultimately generating visible images for human observation.
At the core of the entire system is the infrared detector, which plays a crucial role in achieving infrared imaging. Understanding what makes thermal imaging cameras useful involves knowing the types and characteristics of these detectors. Based on different detection mechanisms, infrared focal plane detectors are generally classified into two categories: cooled detectors and uncooled detectors.
Cooled Infrared Focal Plane Detectors: These rely on low-temperature cooling technology and photon detection principles, requiring cooling devices to maintain a low-temperature environment for optimal performance. Cooled infrared focal plane arrays offer high sensitivity and long detection ranges, making them especially effective in target search and tracking, satellite remote sensing, and advanced scientific research. However, due to the complexity of cooling equipment and materials, they tend to have higher usage costs and power consumption.
Uncooled Infrared Focal Plane Detectors: Composed of pyroelectric detectors or microbolometers along with corresponding circuits and systems, uncooled detectors operate at room temperature without the need for cooling devices. Compared to cooled detectors, uncooled infrared focal plane arrays show clear advantages in size, cost, and lifespan. They are particularly suited for civilian applications that require portability and cost-effectiveness, such as industrial inspection, security monitoring, driver assistance, and consumer electronics.
What Are the Application Advantages of Thermal Imaging Cameras?
As the “eyes that see temperature,” thermal imaging cameras play a critical role in many fields such as industrial monitoring, perimeter security, and scientific research. Understanding what makes thermal imaging cameras useful is key to appreciating their widespread adoption. Their core advantages include:
Stable Detection in Nighttime and Harsh Weather Conditions
What makes thermal imaging cameras useful is their ability to form images by detecting the infrared radiation naturally emitted by objects themselves, without relying on external visible light sources. This enables them to operate reliably in low-visibility environments such as nighttime, dense fog, and smoke, achieving true “all-weather, around-the-clock” monitoring.

Dark Environment

Haze environment
Non-Contact Temperature Measurement for Enhanced Operator Safety
Another key aspect of what makes thermal imaging cameras useful is their ability to measure temperature without physical contact. This is particularly valuable in hazardous environments involving high temperatures, high pressure, toxic substances, or confined spaces. By eliminating the need for close proximity, thermal imaging helps reduce safety risks for personnel.
.jpg)
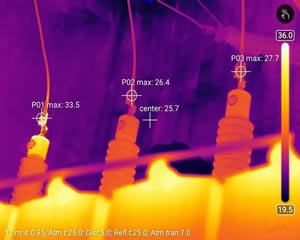
Full-Radiation Thermal Images: One Image Reveals the Whole Problem
Compared to traditional contact-based or spot temperature measurement devices, thermal imaging cameras capture the entire scene’s thermal profile in a single image. This provides a clear and intuitive view of large-area temperature distribution, making it easier to quickly identify overheating, cold spots, or thermal runaway conditions. This powerful visual capability is a major reason what makes thermal imaging cameras useful in both preventive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
Fast Response and Efficient Early Warning Mechanism
What makes thermal imaging cameras useful in real-time applications is their high sensitivity and rapid response speed. In scenarios where quick reaction is critical, thermal cameras can instantly detect abnormal temperatures or behaviors and trigger alarm systems without delay. This enables users to take timely action and prevent potential hazards before they escalate.
Passive Detection with High Concealment
One of the reasons what makes thermal imaging cameras useful for surveillance and security is their passive detection capability. Instead of actively emitting signals, they passively receive infrared radiation from objects to form images. This makes their operation discreet and difficult to detect, making them ideal for perimeter control, covert monitoring, and other applications where stealth is essential.

Long-Range Detection with Clear and Stable Imaging
What makes thermal imaging cameras useful in large-scale monitoring scenarios is their ability to deliver clear imaging and accurate temperature measurement from a distance. Thanks to high-sensitivity detectors and advanced infrared optical systems, thermal cameras can perform effectively even at long ranges. This makes them ideal for monitoring expansive areas such as oil tank zones, substations, and forest fire prevention zones.

Long-distance fire identification
Recommended Products by Raythink
To meet the needs of various scenarios, the market has seen the emergence of numerous high-performance thermal imaging devices that effectively enhance monitoring accuracy and response speed. Below are two representative Raythink thermal imaging products that demonstrate what makes thermal imaging cameras useful in practical applications:
- TN460U Online Ultra-high Temperature Thermal Camera is a non-contact infrared thermal camera specially designed for ultra-high temperature measurement needs. It adopts an uncooled infrared FPA detector, featuring a high resolution of 640×512 and an ultra-wide temperature measurement range of 0~2000°C.
- It features in compact and lightweight design, optional air-cooled/water-cooled shell, and a maximum tolerable ambient temperature of 220°C. A variety of lenses are available to provide clear and accurate infrared images and temperature measurement functions. Adopting open network protocols, it facilitates integration and secondary development for customers to improve system flexibility.
- The PC4 Series Dual-Spectrum PTZ Camera is a medium-to-long-range observation and monitoring product that integrates infrared thermal imaging, an HD visible light camera, and an intelligent PTZ into one.
- It supports intelligent functions such as fire point detection, tripwire intrusion, and regional intrusion detection, enhancing target recognition accuracy during nighttime and adverse weather conditions.
- It is suitable for scenarios requiring wide-range and long-distance monitoring, such as forest fire prevention, airports, and urban high-altitude observation.
Conclusion: Partner with Raythink to Shape a Brighter Future in Thermal Imaging
With continuous advancements in infrared technology, thermal imaging is evolving from a specialized, high-end solution into a more accessible and intelligent tool, widely applied in smart security, industrial inspection, healthcare, and beyond. It breaks through the limitations of traditional vision by allowing us to “see” temperature data invisible to the naked eye. Thanks to its high sensitivity and all-weather performance, thermal imaging plays a vital role in enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
As a leading expert in the field of infrared thermal imaging, Raythink offers a comprehensive product portfolio designed to meet the diverse needs of various industries. Looking ahead, as innovation drives new applications and broader adoption, Raythink will continue to lead the way—powering smarter cities, efficient energy management, and stronger environmental protection.
What makes thermal imaging cameras useful is not just the technology itself, but how it empowers users across sectors to see more, know more, and act faster.
We invite you to contact us anytime for expert product selection advice and technical support, and join us in unlocking a new era of “seeing temperature.
For more information contact sales@raythink-tech.com
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow
Featured Product



